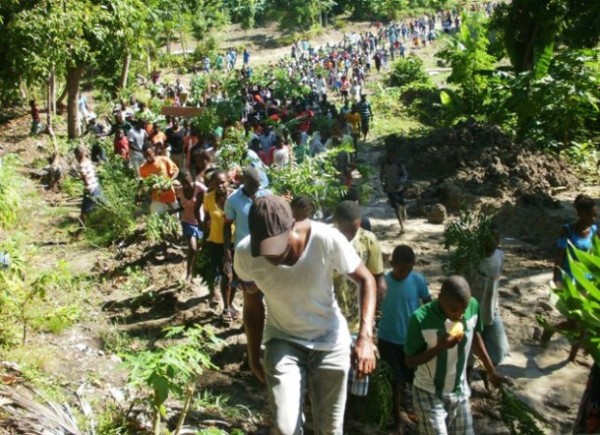
While Ile à Vache, a 20-square mile island off of Haiti’s southern coast, has been promoted as a jewel of Caribbean ecotourism, the subsistence fishermen and farmers of the island have been ignored. As the government moves forward with development plans, the people have responded with a series of protests.


Haiti “Open for Business,” Like it or Not
By Mark Schuller and Jessica Hsu, Published in Common Dreams
Recently Haiti President Michel Martelly celebrated his third year in office. He gained wide support from the U.S. on his election platform which persists as his administration’s slogan: “Haiti is open for business.” Three days after his inauguration, Martelly landed at Île à Vache’s Abaka Bay resort and extended an offer of one million dollars to become 51% shareholder to then-owner Robert Dietrich.
Tourism is a leading industry in the Caribbean. Two models predominate, an upscale “all-inclusive” or a “spring break,” “anything goes” model. While these tourist models may increase foreign exchange, they also rendered many landless, degraded local environments, and triggered conflicts. While foreign owners gain a lot of wealth, many workers receive miniscule minimum salaries. This has been evidenced by the recent struggles by factory workers in Haiti.
Trying to promote “responsible tourism” is the focus of a summit in July in Grenada.
“KOPI advocates a kind of ecotourism that would preserve the nature of the island and also be inclusive. This would be really beneficial to all strata of the population, not just hoteliers. An ecotourism plan could, without excluding some luxury hotels, offer cottages and restaurants that are run by residents of the island, which would directly help the local economy. Why not help the people to start businesses that will preserve the island’s culture and unique atmosphere?” — Jerome Genest, Konbit Peyizan Ilavach (KOPI)
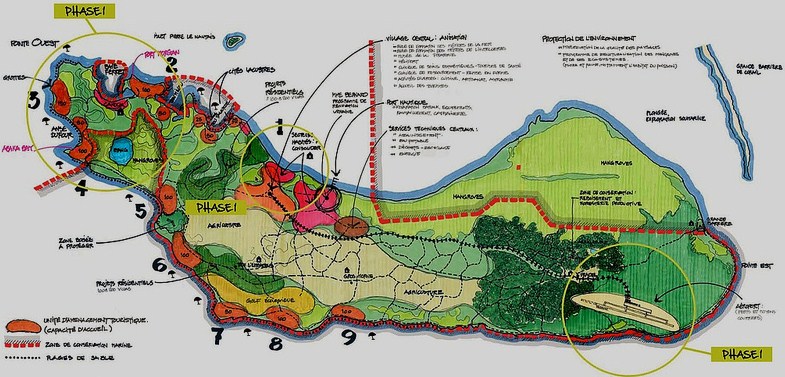

The Haitian government is presenting the “Tourism Destination Île à Vache” project as one such positive model. Minister of Tourism Stephanie Balmir Villedrouin and many other officials have reported to the press and other international audiences that the population of Île à Vache is largely in support of this development project.
If this holds true, then why have thousands mobilized in several protests with some individuals engaging in direct action? And what are viable and responsible solutions?
The islanders undertook a series of protests in which they blocked the roads to paralyze all business activity and construction work on the island. “Ile a Vache is not for sale, not in bulk not in retail,” they chanted. Soon a group of paramilitaries appeared, who began to attack the people in advance of their protests. — Dady Chery, News Junkie Post
On Thursday, May 29, representatives of the Haitian government met with human rights organizations who had published an April report, to attempt to answer these questions.
According to a government representative who attended this meeting, Secretary of State for Plant Production, Fresner Dorcin, reported that he felt his life was in danger as people threw rocks at him during a visit to the island. On a March 1 visit, Minister of Tourism Villedrouin requested that the population stop protesting and send petitions instead. This official stated that a small group of people have been manipulating the population against the project.
However, Laine Marc Donald, the president of the Konbit Peyizan Ilavach (KOPI, Organization of Ile à Vache Farmers), said, “If this is the case then why were three thousand people protesting on December 27, another 8,000 on January 3, and 7,000 on February 7?”
STORY: Haiti: Rebuilding Sustainably with Earthbag Houses


“Dialogue is the Way to Development”
Two religious leaders, including the head of the Catholic parish and a Canadian nun who has been on Île à Vache since 1981, are equally concerned about the government’s proposal.
While Minister Villedrouin has visited the island more than three times, religious leaders were not invited which in Haiti is an effective way to relay messages to the community. Brother Elius said that there was never an open discussion with the population about the project: “dialogue is the way to development.”
Sister Flora Blanchette said that, “People overseas know more about what’s going on here than residents. And that’s a big problem.”
Residents’ concerns about the plan do not stop at the lack of information. On May 10, 2013, Le Moniteur, the official journal of the government published a decree declaring the island a tourist area and private property not recognized. Residents understand that this decree signed by President Martelly, Prime Minister Lamothe and other government officials leaves them vulnerable to exploitation, especially in a process in which they have not been invited to participate.
There are significant environmental concerns. In a country with only an estimated two percent of its original forest cover, Île à Vache contains a large old-growth forest. On August 20, 2013, ground was broken on a new international airport, on this site. Thousands of trees were cut down to construct the airstrip.
That same day, Martelly-appointed interim Mayor Fritz Cesare issued an additional decree forbidding any personal construction without prior authorization.
“Ile a Vache has a total of 10 beaches. If the government takes possession of all of them for its tourism plan, there’ll be no access for fishermen and the general public. Currently, the fishermen continue to fish as they’ve always done. We still don’t know what will happen if the project gets implemented.” — KOPI member Jerome Genest
Clear demands have been made for information but instead the government has responded by sending riot police to quell dissent. On February 25, when citizens peacefully protested the arrest of Jean Matelnus Lamy, riot police shot live ammunition. Twelve people were injured and two others arrested. Other incidences of physical intimidation occurred when blockades were set up earlier in the month. Also, KOPI member Kenold Alexis’s house was ransacked by the island’s mayor and CIMO (riot police). Alexis went to the justice of the peace, who handwrote a declaration of loss of 20,000 gourdes, around $450.
Similarly, in the evening of March 26, 2014, crews of Dominican company Ingeneria Estrella ripped through several areas to build a road without warning. Some of the residents lost as many as 18 coconut trees affecting the livelihood of families according to KOPI spokesperson and director of the high school Feores Jeanty.
Several individuals stated that they are not opposed to the road since it would facilitate smoother transport of commerce and emergency medical transport. The problems are there is no hospital on the island and compensation for losses required by sections 36.1 and 36.2 of Haiti’s constitution have been nullified by the May 10 decree.


Rights to Live, Farm, and Fish
Article 2030 of Haiti’s Civil Code guarantees the right of ownership if an individual has paid rent on the land for ten years. After 20 years of occupancy whether or not rent has been paid, the parcel is granted to the individual or family. So according to Haitian law 102-year-old Isanne Aregran, who was born in her current home, should be secure.
Residents are not necessarily opposed to “development” or tourism. Instead, they are deeply concerned that they will be stripped of their land and no longer have access to the waters in which they fish. Fishing and agriculture are the primary economic engines which the plan appears to threaten.
“The area where the airport runway was constructed has been removed from the public as a commons: a place that could be considered a surplus area for the benefit of the population. Let me explain. In that area, there used to beehives; vegetables like yuca and potatoes, fruit trees and even fungi, djondjon, were cultivated. It was also a place to graze sheep and goats. It was, in short, a place where people could grow and gather in addition to what they grew on their own lands. This allowed them a surplus that was well appreciated.” — Jerome Genest
The inhabitants, especially peasants, underscore the importance of agriculture for their livelihood and the country’s real development. Like the Free Trade Zone on the border with the Dominican Republic, the Caracol industrial park, and mining in the North; Île à Vache is considered very productive agricultural land. For all its displacement and $22 million price tag, only 2,590 people worked in Caracol by the end of 2013. Stripping peasants of their rights to their land and production is a direct affront to Haiti’s food sovereignty.
Île à Vache is not alone: on the mainland, hundreds of peasants in Picot are threatened with forced eviction and loss of livelihood to pave the way for a new international airstrip for Aux Cayes’ airport. Both top-down development projects violate the Food and Agricultural Organization Voluntary Guidelines on the Responsible Governance of Tenure.
Joseph Matelnus Lamy, who is the father of arrested police officer, who was born on the island, theorized a common root of his son’s civil rights and all residents’ land rights being violated: “Without the support of the U.S. government, this Haitian government wouldn’t be around.”
Mark Schuller is Assistant Professor of African American Studies and Anthropology at York College, the City University of New York and Faculté d’Ethnologie, Université d’État d’Haïti. Among several other publications in the public and scholarly arena, Schuller co-edited Capitalizing on Catastrophe: Neoliberal Strategies in Disaster Reconstruction and co-directed documentary Poto Mitan: Haitian Women, Pillars of the Global Economy. He chairs the Society for Applied Anthropology’s Human Rights and Social Justice Committee.
Jessica Hsu is a graduate student of anthropology and the coordinator for Another Haiti is Possible with Other Worlds.













Pingback: Haiti Land Grab
Pingback: Dominican Republic: Modern Day Sugarcane Slavery | WilderUtopia.com